- Overwrite
- Posts
- What are Physically-Backed Non-Fungible Tokens?
What are Physically-Backed Non-Fungible Tokens?
Opportunities for investors and collectors
What Are Physically-Backed NFTs?

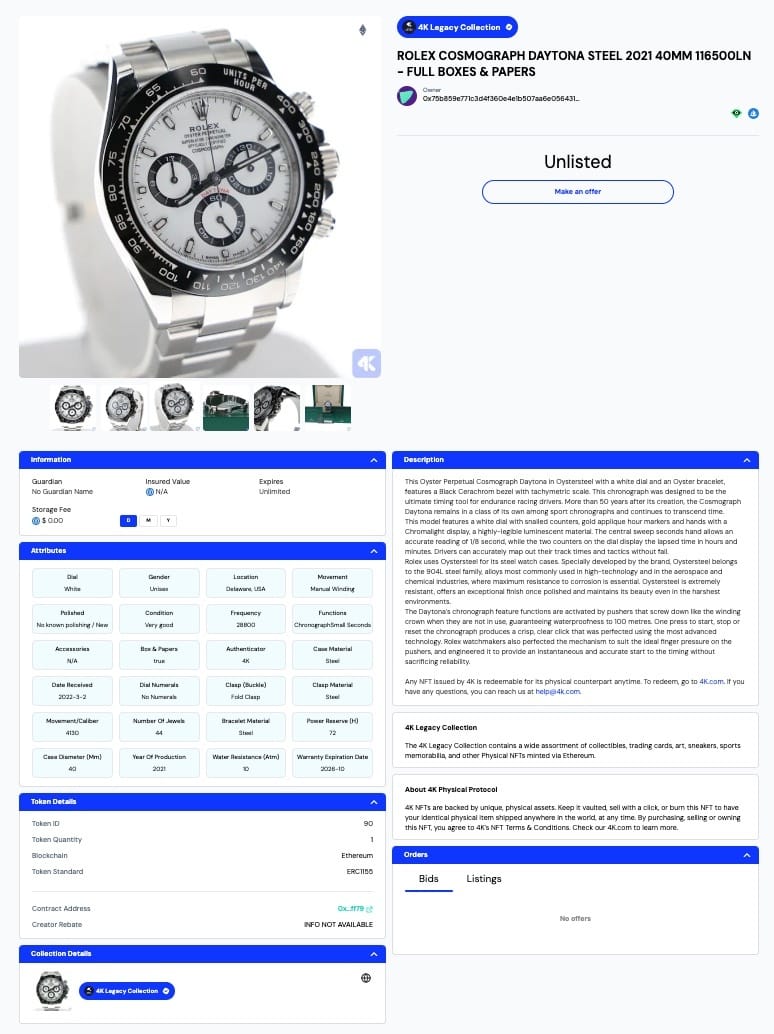
A physically-backed non-fungible token (NFT), combines the digital world of NFTs with physical assets. It represents a unique digital token that is linked to a physical item or asset in the real world.
Examples include:
Wine
Watches
Cars
Luxury goods
Rare coins
Jewellery
Classic cars
Real estate
Instruments
The concept behind physically-backed NFTs is to provide investors or collectors with the ownership of a physical item along with a corresponding digital token that represents authenticity, provenance, or additional features like exclusive perks and ‘members-only’ access to events or future product sales. The physical item can be stored securely, while the NFT can be easily traded, transferred, or displayed digitally on marketplaces.
Why are Physically-Backed NFTs Important?
Imagine a physically-backed NFT representing a Rolex. The digital token would serve as proof of ownership and provide the holder with the opportunity to unlock latent capital by taking a loan against the value of the watch via protocols like arcade.xyz.
Physically-backed NFTs provide a bridge between the digital and physical worlds, adding value and liquidity to collectibles and other alternative assets that exist on the edges of traditional financial markets.
They offer opportunities for investors and collectors to participate in the NFT market while also having a tangible asset associated with their digital ownership.
What Benefits do Physically-Backed NFTs provide?
Increased Liquidity and Fractional Ownership:
NFTs allow for their fractional ownership, so investors can participate with smaller amounts of capital which can increase liquidity in traditionally illiquid markets.
Established platforms enable investors to trade more easily, potentially attracting a broader range of participants and increasing overall market liquidity.
Accessible Investment Opportunities:
NFTs can provide opportunities for investors to gain exposure to asset classes that were previously inaccessible or had high barriers to entry. Like real estate, the luxury goods market or high end wine.
Global Market Access:
The crypto market provides a global and decentralized platform, allowing investors from various geographic locations to invest. This opens up opportunities for cross-border investments and broadens the investor base.
Enhanced Transparency and Efficiency:
On-chain data allows investors to verify ownership, track transactions, and access asset information while reducing intermediaries and improving efficiency in the asset transfer process.
Platforms can streamline processes, reduce paperwork, and potentially lower transaction costs. Smart contracts can automate certain aspects of transactions and increase overall market efficiency.
Enhanced Security and Ownership Rights:
Security and transferability are inherent properties of NFTs, plus ownership rights and digital proof of assets can be established on-chain.
Final Thoughts on Physically-Backed NFTs

While physically-backed NFTs present intriguing opportunities to tokenize real-world assets and expand trading opportunities for investors, this emerging use case also faces hurdles regarding;
Unproven security and custody models
Regulatory uncertainty
Valuation complexities
Platform risks
However, the capabilities enabled by blockchains like Ethereum give physically-backed NFTs a valid value proposition if executed responsibly.
Overall, recent developments in the NFT space have represented an experimental period for asset-backed NFTs that have laid the groundwork for future growth. As the business models and technical infrastructure mature over time, asset-backed NFTs have disruptive potential to transform ownership and access across a range of previously illiquid markets.
But realizing this potential hinges on thoughtful governance, technology developments, and clear regulatory guidance to instill credibility and trust among mainstream institutions and investors.